When it comes to the packaging and transportation of goods, the choice of strapping material is crucial for ensuring the safety and stability of goods.
Two of the most commonly used materials in the industry are steel and plastic strapping, each offering unique benefits and serving different purposes based on the nature of the load and the requirements of the supply chain.
Steel strapping, known for its exceptional strength and durability, has been a traditional choice for securing heavy or irregularly shaped loads. Its robust nature makes it suitable for applications where high tensile strength and minimal stretch are essential. On the other hand, plastic strapping, with its flexibility and lighter weight, is increasingly popular for bundling lighter items. It offers a range of benefits, including ease of handling and a lower risk of injury, making it a favourable choice for certain packaging needs.
To help you find the right option for your needs, we have put together this article. We’ll be comparing steel and plastic strapping so you can understand their strengths, limitations and ideal applications.
Steel Strapping vs Plastic Strapping
First up, let’s look at the characteristics and uses of steel strapping and plastic strapping:
Steel Strapping
What is steel strapping?
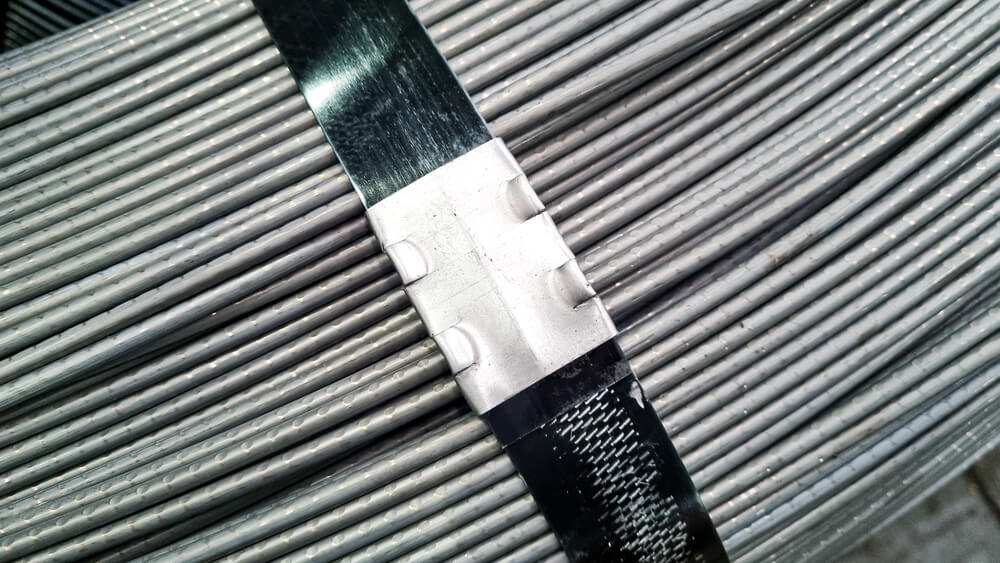

Steel strapping is a robust packaging material, widely recognised for its strength and reliability in securing heavy loads. Made from high-tensile steel, it is designed to withstand extreme conditions without compromising its integrity. This makes it an ideal choice for a variety of heavy-duty applications in logistics and shipping.
Key characteristics of Steel Strapping:
- High Tensile Strength: Steel strapping is extremely strong, capable of holding together heavy and bulky items securely. Its high break strength means it is less likely to snap or tear under tension.
- Minimal Elongation: Unlike other materials, steel strapping does not stretch significantly once applied. This property is crucial for loads that must remain tightly secured without shifting during transit.
- Durability: Resistant to UV radiation, heat, and corrosion, steel strapping maintains its strength over time, even in harsh environmental conditions.
Typical uses of steel strapping:
- Industrial and Construction Materials: Often used for strapping heavy construction materials like bricks, steel beams, and large machinery parts, steel strapping ensures these items stay bound and immobilised during transport.
- Heavy Manufacturing: In the manufacturing sector, especially in the metal and automotive industries, steel strapping is essential for bundling products like steel coils, metal sheets, and automotive components.
- Shipping and Exporting Heavy Goods: For goods that travel long distances, especially overseas, the durability and strength of steel strapping make it an excellent choice for ensuring the load remains secure throughout the journey.
The strength and durability of steel strapping make it a go-to material for heavy-duty applications where the safety and security of the load are of utmost importance. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions and maintain its hold on heavy, unwieldy items makes it an indispensable tool in industries that handle substantial products.
Plastic Strapping
What is plastic strapping?
Plastic strapping is a versatile and cost-effective solution for securing a wide range of goods in the packaging and logistics industry. Made from materials such as polypropylene and polyester, plastic strapping offers a combination of flexibility and strength, making it suitable for a variety of applications, particularly where heavy-duty steel strapping is not necessary.
Key characteristics of Plastic Strapping:
- Flexibility: One of the main advantages of plastic strapping is its ability to stretch and conform to the shape of the load. This elasticity allows the strap to maintain a snug fit, even as packages settle or shift slightly during transit.
- Lightweight Nature: Plastic strapping is significantly lighter than steel strapping, reducing overall package weight and making it easier to handle. This can be especially beneficial in reducing shipping costs and minimising the physical strain on workers.
- Variety of Strengths: While not as strong as steel, plastic strapping comes in various grades, each designed to meet different load requirements. High-strength polyester strapping, for example, can be an excellent alternative for moderately heavy loads.
Typical uses of plastic strapping:
- Palletising Consumer Goods: Frequently used for bundling lighter items such as boxed products, consumer goods, and textiles. Its flexibility ensures that products are tightly secured without damage.
- Securing Paper and Print Materials: Ideal for bundling newspapers, magazines, and other paper products, where the risk of damage from overly tight strapping needs to be minimized.
- Logistics and Distribution: In distribution centres, plastic strapping is widely used for securing items onto pallets for internal movement and short-haul transportation. Its ease of use and efficiency make it a popular choice in these settings.
Plastic strapping’s flexibility, lightweight nature, and range of strengths make it a versatile choice for securing less heavy loads. Its suitability for a diverse array of applications ensures that it remains a popular option in many sectors of the packaging and logistics industry.
Comparing the Strength and Durability of Plastic and Steel Strapping
When selecting the right strapping material for packaging and logistics, understanding the differences in tensile strength and durability between steel and plastic strapping is crucial. Each material is uniquely suited to different types of loads based on these characteristics.
Tensile Strength Comparison:
– Steel Strapping: Known for its exceptional tensile strength, steel strapping is capable of securing extremely heavy and bulky items. It is less likely to stretch or break under tension, making it ideal for loads that require robust and rigid support.
– Plastic Strapping: While plastic strapping offers lower tensile strength compared to steel, it provides adequate strength for lighter loads. Its ability to stretch slightly makes it ideal for loads that may compress or settle, such as pallets of boxed goods.
Durability Aspects:
– Steel Strapping: Highly durable, steel strapping can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to UV light, moisture, and extreme temperatures. It is less prone to wear and tear over time, maintaining its strength for long-term or rough transportation.
– Plastic Strapping: Plastic strapping is less durable in extreme environmental conditions but offers sufficient durability for indoor storage and shorter transit periods. Its resilience against corrosion makes it suitable for certain applications where steel might be less ideal.
Suitability for Different Loads:
– Steel Strapping: Best suited for very heavy, rigid, or high-value loads, such as construction materials, heavy machinery, and metal products. Its strength ensures these loads remain immovable and secure during transportation.
– Plastic Strapping: Ideal for lighter, more uniform loads, such as consumer goods, palletised boxes, and paper products. It provides a secure hold while protecting the goods from damage due to over-tightening.
Your choice between the two strapping options should largely be made based on the specific requirements of the load in question.
Cost Considerations of Plastic and Steel Strapping
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of strapping materials is a critical aspect – both steel and plastic strapping have different cost implications in terms of initial investment and long-term savings.
Initial Costs:
– Steel Strapping: Generally, steel strapping is more expensive in terms of initial cost compared to plastic strapping. This is due to the material’s strength and durability. The tools required for steel strapping (tensioners, sealers, cutters) are also typically more robust and expensive.
– Plastic Strapping: Plastic strapping offers a more budget-friendly initial investment. The material itself is less expensive, and the tools for plastic strapping are often cheaper and simpler than those used for steel strapping.
Long-Term Savings and Efficiency:
– Steel Strapping: While the upfront cost is higher, steel strapping can be more cost-effective in the long run for certain applications, especially where high strength and durability are required. Its ability to secure heavy loads reduces the risk of damage and loss, which can translate to significant savings.
– Plastic Strapping: For businesses with lighter packaging needs, the lower cost of plastic strapping can be economical. However, it may require more frequent replacement than steel strapping, which could offset some of the initial savings over time.
While steel strapping may have a higher initial cost, its durability and strength can offer long-term savings for heavy-duty applications. Plastic strapping, being more affordable upfront, can be a cost-effective choice for less demanding applications, but it’s essential to consider the potential need for more frequent replacements.
Environmental Impact of Steel and Plastic Strapping
In today’s environmentally conscious business landscape, understanding the ecological implications of packaging materials like steel and plastic strapping is crucial. Both materials have distinct environmental footprints and recyclability aspects, which can influence a business’s choice in favour of more sustainable practices.
Recyclability and Environmental Footprint
- Steel Strapping: Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world, which lends a significant environmental advantage to steel strapping. It can be melted down and reformed without losing its strength, making it a sustainable choice in terms of recyclability. However, the production of steel strapping requires significant energy and resources, which is a consideration in its overall environmental impact.
- Plastic Strapping: The recyclability of plastic strapping varies depending on the type of plastic used. Polypropylene strapping, for instance, is more easily recycled than polyester. However, the recycling rates for plastic are generally lower than for steel, and the environmental impact of plastic waste is a growing concern. The production of plastic strapping also involves the consumption of fossil fuels, contributing to its carbon footprint.
The environmental impact of strapping choices is an important consideration for businesses aiming to minimise their ecological footprint.
Safety and Handling of Plastic and Steel Strapping
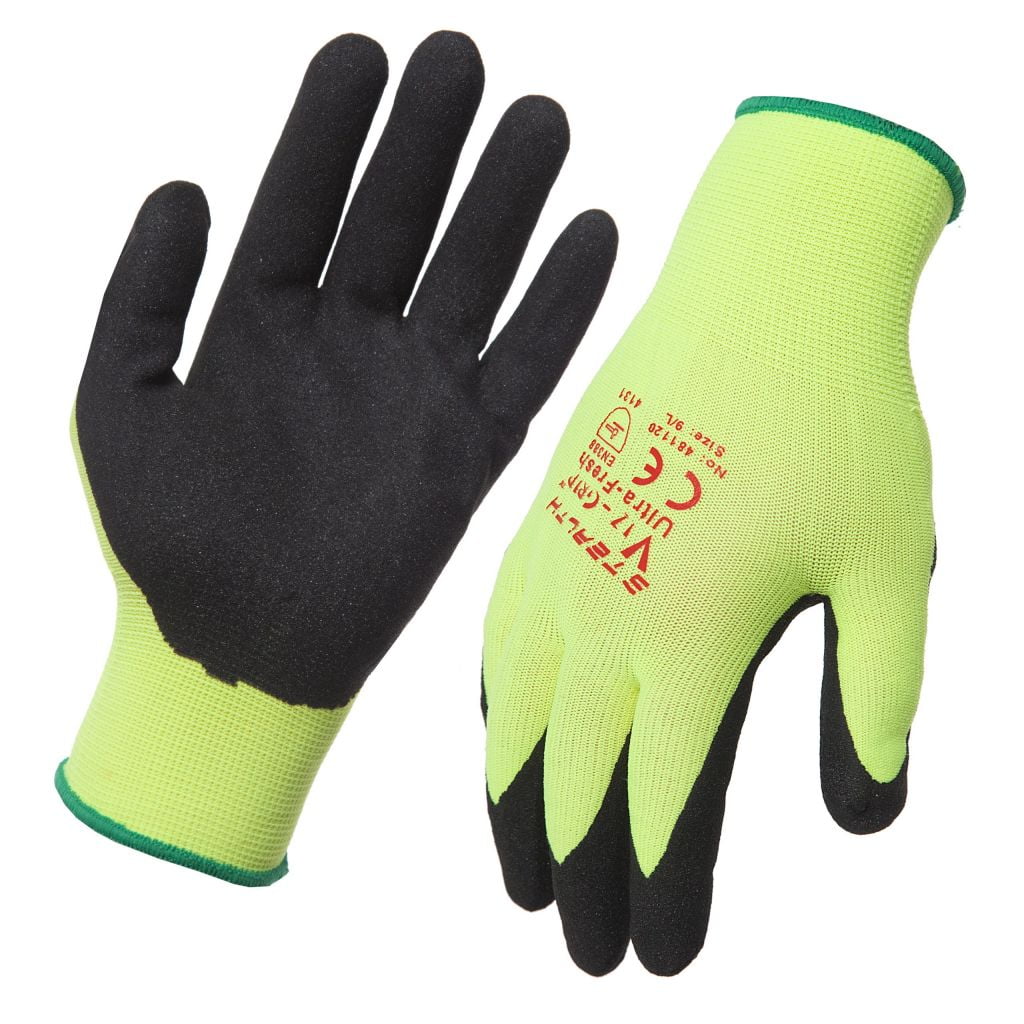

Safety is a paramount concern when working with strapping materials. Both steel and plastic strapping have unique safety considerations, and understanding these can help prevent workplace injuries.
Safety Aspects of Steel vs. Plastic Strapping:
Steel strapping is very strong and can pose a risk of injury if not handled correctly. The edges of steel straps can be sharp, and there is a risk of the strap snapping under tension, which can cause serious injury. Additionally, the tools used for steel strapping are more complex and require careful handling.
Plastic strapping is generally safer to handle than steel. It is lighter, and the edges are not as sharp, reducing the risk of cuts. However, there is still a risk of injury if the strapping snaps or if tools are used improperly.
Tips for Safe Handling and Application:
For Steel Strapping:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Be cautious of sharp edges and ensure that the strap ends are properly secured.
- Use the correct tools for tensioning and sealing the strapping, and ensure they are maintained and used as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Be aware of the tension in the strap and stand clear when cutting or tensioning to avoid snap-back injuries.
For Plastic Strapping:
- While plastic strapping is generally safer, wearing gloves can still help prevent abrasion injuries.
- Ensure that the strapping is tensioned correctly – not too loose, but also not overly tight to prevent snapping.
- Use the appropriate tools for your type of plastic strapping and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe use.
Not Sure Which Strapping is Right For You?
If you need strapping materials in your business but you’re not sure where to start, get in touch with us here at Melbourne Packaging Supplies. We have more then 40 years of experience in the packaging industry and we can help you find the right strapping option to suit your needs and all the tools and accessories you need.



Recent Comments